பயனர்:Shriheeran
்கள்
[தொகு]| Letter name (Unicode) |
Variants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modern Hebrew | Ancestral | |||||||
| Serif | Sans- serif |
Mono- spaced |
Cursive | Rashi | Phoenician | Paleo-Hebrew | Aramaic | |
| Alef | א | א | א | 
|
||||
| Bet | ב | ב | ב | 
|
||||
| Gimel | ג | ג | ג | 
|
||||
| Dalet | ד | ד | ד | 
|
||||
| He | ה | ה | ה | 
|
||||
| Vav | ו | ו | ו | 
|
||||
| Zayin | ז | ז | ז | 
|
||||
| Het | ח | ח | ח | 
|
||||
| Tet | ט | ט | ט | 
|
||||
| Yod | י | י | י | 
|
||||
| Kaf | כ | כ | כ | 
|
||||
| Final Kaf | ך | ך | ך | 
| ||||
| Lamed | ל | ל | ל | 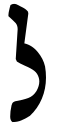
|
||||
| Mem | מ | מ | מ | 
|
||||
| Final Mem | ם | ם | ם | 
| ||||
| Nun | נ | נ | נ | 
|
||||
| Final Nun | ן | ן | ן | 
| ||||
| Samekh | ס | ס | ס | 
|
||||
| Ayin | ע | ע | ע | 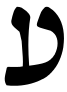
|
||||
| Pe | פ | פ | פ | 
|
||||
| Final Pe | ף | ף | ף | 
| ||||
| Tsadi | צ | צ | צ | 
|
||||
| Final Tsadi | ץ | ץ | ץ | 
| ||||
| Qof | ק | ק | ק | 
|
||||
| Resh | ר | ר | ר | 
|
||||
| Shin | ש | ש | ש | 
|
||||
| Tav | ת | ת | ת | 
|
||||
Yiddish symbols
[தொகு]| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| வார்ப்புரு:Hebrew | These are intended for Yiddish. They are not used in Hebrewவார்ப்புரு:Ref label. |
| வார்ப்புரு:Hebrew | The rafe (வார்ப்புரு:Hebrew) diacritic is no longer regularly used in Hebrew. In masoretic manuscripts and some other older texts the soft fricative consonants and sometimes matres lectionis are indicated by a small line on top of the letter. Its use has been largely discontinued in modern printed texts. It is still used to mark fricative consonants in the YIVO orthography of Yiddish. |
2008இல் சர்வாதிகாரம்
[தொகு]21st century
[தொகு]2001
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Essential Harvest | August – November | A terrorist group known as the National Liberation Army terrorise the town of Tetovo in present-day Republic of Macedonia. The Macedonian armies are later helped by NATO to disarm the National Liberation Army. |
| Battle of Mazar-e-Sharif | 9 November | United States and Northern Alliance forces defeat Taliban forces in the city as part of the U.S. Invasion of Afghanistan. |
| Battle of Herat | 12 November | Special Operations Forces of the United States and the ஈரான் assist the Afghan Northern Alliance in seizing Herat from the தாலிபான் amidst a coordinated insurrection and local uprising. |
| Battle of Kabul | 13–14 November | Northern Alliance and US forces attack Kabul and capture it from the Taliban. |
| Battle of Tarin Kowt | 13–14 November | ஹமித் கர்சாய்'s Eastern Alliance together with US forces defend the town of Tarin Kowt from the Taliban. |
| Battle of Kandahar | 22 November – 7 December | A force of local militia under Pashtun military commanders and their American advisers capture the last major city under Taliban control. |
| Battle of Qala-i-Jangi | 25 November – 1 December | Northern Alliance fighters, assisted by British and American Special Forces, quell an uprising of foreign Taliban prisoners. |
| Battle of Tora Bora | 12–17 December | Coalition and Northern Alliance forces besiege Al-Qaida forces. Presumably, உசாமா பின் லாதின் was present, but escaped. |
2002
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Anaconda | 1–19 March | The largest land battle between US forces and Taliban militia ends in an unsuccessful US attempt to dislodge the Taliban from their mountain strongholds |
| Operation Defensive Shield | 29 March – 3 May | இசுரேல்i operation in the மேற்குக் கரை, aimed to halt Palestinian suicide bombings against civilians in Israel during the Second Intifada, which results in extensive damage to terrorist infrastructure and an important decrease of Palestinian attacks: |
| Battle of Jenin | 3–11 April | இசுரேல் defeats Palestinian militants in the city of Jenin. |
| Battle of Bethlehem | 2 April – 10 May | இசுரேல் occupies Bethlehem and tries to capture wanted Palestinian militants who are hiding in the Church of the Nativity. |
| Battle of Nablus | 5–8 April | இசுரேல் defeats Palestinian militants in the city of Nablus. |
2003
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Nasiriyah | 23–29 March | American armored and mechanized units force a crossing over the புராத்து ஆறு, despite stiff resistance from the ஈராக்is. |
| Battle of Najaf | 26 March – 3 April | The American 327th Infantry Regiment defeats the Iraqis and takes the city, allowing them to protect vital supply lines for Coalition forces. |
| Battle of Karbala | 27 & 28 March | The American 3rd Infantry Division defeats ஈராக்'s elite Republican Guard, resulting in 200 ஈராக்i casualties. |
| Battle of Baghdad | 3–12 April | American forces capture the Iraqi capital from Saddam Hussein's forces, causing the downfall of his government. |
| Battle of Basra | 6 April | British forces manage to secure the city after a month of some of the fiercest fighting since the outbreak of the war. |
| Battle of Debecka Pass | 6 April | The US forces capture a major crossroad near the village of Debecka in Iraq. |
2004
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Wana | 16–23 March | Part of the Waziristan War, Pakistani army takes over Taliban positions. |
| First Battle of Fallujah | 4 April – 1 May | Also called Operation Vigilant Resolve; US forces attempt to retake Fallujah from the control of Iraqi insurgency, resulting a ceasefire and American withdrawal. |
| Battle of Najaf | 5 April – August | Fighting breaks out in a cemetery near the Imam Ali Mosque in Najaf between United States forces and the Mahdi Army of Muqtada al-Sadr. |
| Operation Rainbow | 18–23 May | Successful Israeli military operation against ஹமாஸ், Islamic Jihad and the பாலிமரேசு தொடர் வினை. |
| Operation Days of Penitence | 30 September – 16 October | Israeli offensive launched into the northern காசா கரை. Israel claims victory after stating its goal of preventing Palestinian militants from firing Qassam rockets into Israeli settlements in Gaza and at the town of Sderot. |
| Second Battle of Fallujah | 7 November – 23 December | Also known as Operation Phantom Fury and Operation al-Fajr; Coalition forces recapture rebel-held Fallujah in the largest post-invasion clash so far in the war. |
2005
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Al Qaim | 8–19 May | Military offensive conducted by the United States Marine Corps, against insurgent positions in Iraq's northwestern Anbar province, ending with US tactical victory. |
| Battle of Nalchik | 13 October | The Yarmuk Jamaat take on Nalchik, கபர்தினோ-பல்கரீயா in Russia. They are defeated by Russian security forces. |
| Second Battle of Adre | 18 December | Rally for Democracy and Liberty attack the government garrison at Adre, Chad. The garrison had been forewarned, and defeats their attackers, taking few casualties. |
2006
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of N'Djamena | 13 April | The Chadian rebel group United Front for Democratic Change attacks the capital city of சாட். The rebels are forced to retreat by the Military of Chad. Chad breaks off relations with சூடான் as a result. |
| Second Battle of Mogadishu | 7 May – 11 July | Militia loyal to the Islamic court union defeats the Alliance for the Restoration of Peace and Counter-Terrorism and takes control of the Somali capital மொகடிசு. |
| Operation Mountain Thrust | 15 May- 31 July | The largest offensive against the தாலிபான் since 2001 is launched by Coalition forces. |
| Operation Together Forward | 14 June – 24 October | The Coalition is unsuccessful in succuring Baghdad and reducing violence. |
| Operation Summer Rains | Since 28 June | Israel enters the காசா கரை searching for soldier கிலாத் ஷாலித், who was abducted in a raid. |
| Zar'it-Shtula incident | 12 July | A cross-border ஹிஸ்புல்லா raid captures two Israeli soldiers. Israeli troops enters லெபனான் in an unsuccessful attempt to get them back. This ignites the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict. |
| Battle of Habbaniyah | 15 July – December | U.S. Marines of the Third Battalion, Second Marine Division, sweep through urban sprawl between Ramadi and Fallujah in a series of operations (i.e. Operations Rubicon and Sidewinder), disrupting flow of அல் காயிதா into both cities, and killng and capturing over 300 insurgents. Action centered around Kilo Company, nicknamed "Voodoo", in the town of Husaybah, on the outskirts of Ramadi, killing 20+ insurgents and capturing/wounding 137, while losing only 4 Marines KIA, 17 WIA. The battalion lost 14 Marines KIA, 50+ WIA. |
| Battle of Bint Jbail | 24 July – 11 August | Israel retreats after attempting to take the town of Bint Jbail in Lebanon, regarding it as a "Hezbollah stronghold". |
| Battle of Ayta ash-Shab | 31 July – 11 August | Israel engages in a firefight with Hezbollas in the Lebanese town of Ayta ash-Shab. |
| Operation Sharp and Smooth | 1 & 2 August | An Israeli airborne operation captures five Lebenese civilians and kills what it claims to be Hezbolla members. |
| 2006 Tyre raid | 4 August | Israel successfully raids Tyre to attack Hezbollah members based there. |
| 2006 Litani offensive | 11–14 August | Israel launches the final offensive in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict to clear Southern Lebanon of as many Hezbolla militants as possible before the ceasefire takes effect. The battle and war end with United Nations Security Council Resolution 1701. |
| Operation Medusa | 2–17 September | Coalition troops attacks the Taliban insurgency, securing a tactical victory. |
| Operation Mountain Fury | 09/16/06 – 01/15/07 | Coalition forces launch a successful follow up to Operation Medusa in an attempt to clear eastern Afghanistan of the Taliban. |
| Battle of Baidoa | 20–26 December | ICU militia battle the Somali Transitional Federal Government. எதியோப்பியாn and TFG troops successfully defend and counterattack against the ICU taking the ICU base cities of Dinsoor and Bur Hakaba. |
| Battle of Bandiradley | 23–25 December | எதியோப்பியாn/புன்ட்லாந்து offensive in Bandiradley, சோமாலியா pushes the Islamic Courts out of the city and opens up a northern front in the Somali Civil War. |
| Battle of Beledweyne | 24–25 December | எதியோப்பியாn offensive towards the city of Jowhar overruns the Islamic Courts stronghold of Beledweyne during the Somali Civil War. |
| Battle of Jowhar | 27 December | எதியோப்பியாn/TFG armoured offensive hits the ICU stronghold of Jowhar, forcing the Islamists to pull back, and bringing the Ethiopians/Government troops within 90 km of மொகடிசு. The battle also effectively flanked and threatened to cut off ICU forces still in the Bay region. |
| 28 December | எதியோப்பியா captures Mogadishu. |
2007
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Ras Kamboni | 5–12 January | The Transitional Federal Government of Somalia, in coalition with Ethiopia and the US, defeats the Islamic Courts Union. |
| Battle of Najaf (2007) | 28–29 January | Iraqi and Coalition forces defeat the Soldiers of Heaven cult. |
| Operation Law and Order | 14 February – 24 November | US troops successfully battle Iraqi insurgents to restore law and order in பக்தாத். |
| Battle of Mogadishu | 21 March – 26 April | Ethiopian, Somalian and Ugandan forces battle the Popular Resistance Movement indecisively. |
| Operation Achilles | 6–30 May | Tactically successful Coalition operation in ஆப்கானித்தான் to clear the Helmand Province of தாலிபான் terrorists. |
| Battle of Nahr el-Bared | 20 May – 7 September | Armed conflict after Fatah al-Islam, an Islamist militant organization, lays siege to the refugee camp of Nahr al-Bared for Palestinians in லெபனான். |
| Battle of Gaza (2007) | 7–15 June | Hamas defeats the Fatah, and takes over the Gaza Strip. |
| Battle of Chora | 15–19 June | Coalition forces capture Chora District in Oruzgan Province from the Taliban. |
| Battle of Musa Qala | 7–12 December | ISAF and Afghan forces capture Musa Qala District in Helmand Province from the Taliban. |
| Battle of Thoppigala | 25 April – 11 June | Sri Lanka Army captures Toppigala Jungle in Estern Province from the LTTE. |
2008
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of the Forward Defence Lines | 2 January – 24 November | Victorious 2008 SLA Northern Offensive in Sri Lanka |
| Battle of N'Djamena | 2–4 February | Forces loyal to the President of Chad defeat a rebellion. |
| Operation Hot Winter | 29 February – 3 March | இசுரேலிய பாதுகாப்புப் படைகள் campaign in the காசா கரை in response to Qassam rockets fired by ஹமாஸ். |
| 2008 Mardakert skirmishes | 4 March | Skirmishes between the unrecognized Nagorno-Karabakh Republic and அசர்பைஜான், victory undecided. |
| Battle of Basra | 25–31 March | Iraqi Army attempt to clear the city of Basra from Mahdi Army militiamen is successful and the Maliki government forces them to cease activities. |
| 2008 attack on Omdurman and Khartoum | 10–12 May | The தார்பூர் rebel group Justice and Equality Movement attack the Sudanese cities of Omdurman and கர்த்தூம் unsuccessfully. |
| 2008 Djiboutian-Eritrean border conflict | 10–13 June | Minor skirmishes between சீபூத்தீ and எரித்திரியா, ending in victory of Djibouti forces. |
| Battle of Arghandab | 18 and 19 June | NATO led forces launch a successful offensive to clear the Taliban out of Arghandab district and from nearby Kandahar. |
| Battle of Wanat | 13 July | Significant American casualties among the defending paratroopers leads to American withdrawal following தாலிபான் early morning attack. |
| Battle of Tskhinvali | 8–10 August | Georgians attack the தெற்கு ஒசேத்தியா city of திஸ்கின்வாலி ending in withdrawal by the Georgians. |
| Battle of the Kodori Gorge | 9–12 August | Georgian civilians flee their homes in Upper Abkhazia. Georgian military engages Abkhazian military forces unsuccessfully. |
| Battle of Goma | 25 October | Part of the ongoing 2008 Nord-Kivu war in the காங்கோ மக்களாட்சிக் குடியரசு. |
| Operation Cast Lead | 27 December – 18 January | Israel launches an air and ground operation to stop ஹமாஸ் from launching of Qassam and Grad rockets from the Gaza Strip. |
2009
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Mullaitivu | 2–25 January | The Sri Lankan army defeats the Tamil Tigers in a battle over the town of முல்லைத்தீவு. |
| Battle of Chalai | 2–6 February | Sri Lankan Army battles Tamil Tigers to capture one of the last Sea Tiger naval bases. |
| Battle of Alasay | 14–23 March | Codename Operation Dinner Out – French and Afghan troops defeat Taliban insurgents in the Alasay Valley. |
| First and Second Battles of Kakarak | 16 March – 12 April | Two battles of Australian forces against Taliban insurgents, both victorious. |
| Battle of Aanandapuram | 29 March – 5 April | Decisive victory of the Sri Lanka military against the தமிழீழ விடுதலைப் புலிகள். |
| Battle of Am Dam | 7 and 8 May | The Chadian Army defeats UFR rebels. |
| Second Battle of Swat | 16 May – 15 July | The Pakistani Army retakes the town of Mingora from the தாலிபான், killing many leaders. |
| Battle of Dahaneh | 12–15 August | US, UK and Afghan troops capture the city from Taliban insurgents. |
| Battle of Kamdesh | 3 October | Taliban insurgents attack a US Combat Outpost. They are repulsed, but the outpost is abandoned due to damage. |
| Battle of Daecheong | 10 November | Clash between South and North Korean naval troops at the Northern Limit Line, ending in a victory for the South. |
| Operation Cobra's Anger | 4–7 December | Successful US-led offensive in Helmand province in southern Afghanistan. |
2010
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Moshtarak | 13 February – 7 December | ISAF pacification offensive in the area that is described as the "poppy-growing belt" of Helmand Province in southern Afghanistan. |
| Battle of Mogadishu | 10 March – 18 April | The eighth recognised battle over மொகடிசு since 1993. |
| Battle of Derapet | 24 August | A combined Australian Army and Afghan National Army patrol defeats Taliban forces. |
| Operation Bulldog Bite | 12 November | Joint U.S. and Afghan counter-insurgent mission in Kunar province, Afghanistan, against Taliban forces. |
2011
[தொகு]| Battle | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Dawn of Gulf of Aden | 16–21 January | The South Korean Navy rescues the crew of the hijacked Samho Jewelry, killing eight Somali pirates. |
| First Battle of Benghazi | 17–20 February | Libyan rebel forces free the city from Col. Gaddafi's rule – First battle of the 2011 லிபிய உள்நாட்டுப் போர். |
| Battle of Misrata | 18 February – 15 May | After Months of intense fighting, the rebels take full control of the city, supported by NATO aircraft. |
| First Battle of Zawiya | 24 February – 10 March | The city is retaken by Libyan elite soldiers, one of the rebels' commanders is killed. |
| First Battle of Brega | 2 March | pro-Gaddafi troops fail to retake the city from rebel forces. |
| Battle of Ra's Lanuf | 4–12 March | After initial success by the rebel forces, the city is retaken by government troops. |
| Battle of Bin Jawad | 6 March | Gaddafi forces retake the city – the initial Rebel offensive westwards is halted. |
| Second Battle of Brega | 13–15 March | The city is retaken by Gaddafi forces after the defeats at Ra's Lanuf and Bin Jawad. |
| Battle of Ajdabiya | 15–26 March | Initial success by government troops is halted and they are pushed back by rebels, under fire from NATO aircraft. |
| Second Battle of Benghazi | 19–20 March | Loyalist forces fail to recapture Benghazi from the now UN-backed rebels. |
| Third Battle of Brega | 31 March – 7 April | A rebel advance on Brega is repelled with heavy artillery, Pro-Gaddafi forces march on Ajdabiya. |
| Battle of Brega-Ajdabiya road | 8 April – 13 July | Advances on Brega and Ajdabiya by the opposing forces lead to a stagnant frontline in-between the two cities. |
| Battle of Kandahar | 7–9 May | The city is besieged by Taliban insurgents, Afghan Police Forces are able to fend them off. |
| Battle of Sana'a | 23 May – 7 June | Hashid tribal forces under Sheikh Sadiq al-Ahmar fight Army troops loyal to president Saleh, resulting in a cease-fire. |
| Battle of Do Ab | 25 May | US and Afghan government troops are ambushed by தாலிபான் insurgents and kill most of the attackers. |
| Fourth Battle of Brega | 14 July – 22 August | After initial victories of pro-Gaddafi forces, rebels take the city in late August. |
| Second Battle of Zawiya | 13–20 August | Rebel forces capture Zawiya and advance on Tripoli. |
| Battle of Tripoli (2011) | 20–28 August | Tripoli is captured by rebel forces, Gaddafi government collapses. |
| Battle of Bani Walid | 8 September – 17 October | Initially, pro-Gaddafi forces fend off anti-Gaddafi forces but on 9 October anti-Gaddafi forces launch a new offensive against the defenders, taking the city by 17 October. |
| Battle of Sirte (2011) | 15 September – 20 October | National Liberation Army soldiers attack the last capital of the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya and take it on 20 October. Colonel முஅம்மர் அல் கதாஃபி also dies this day. |
முடியாட்சி
[தொகு]பண்டைக்காலம்
[தொகு]- எகிப்து (c. 3500 BC - 30 BC)
- Kingship of Tara (c. 3,400 BC - 1022 AD)
- மினோவன் நாகரிகம் (c. 2600 BC - 1200 BC)
- Gojoseon (c. 2333 BC - 108 BC)
- அக்காடியன் பேரரசு (Akkadian Empire) (c. 23rd century BC - c. 21st century BC)
- பாபேல் (1959 BC - c. 6th century BC; பாரசீகப் பேரரசால் எடுக்கப்பட்டது)
- மைசீனியன் கிரீஸ் (Mycenaean Greece) (c. 1600 BC - c. 1100 BC)
- இசுரயேல் அரசு (ஒன்றிணைந்த முடியாட்சி) of Israel (c. 1050 BC- c. 930 BC); succeeded by the following two kingdoms:
- Kingdom of Israel (c. 930 BC- 722 BC; அசிரியாவினால் வெற்றிகொள்ளப்பட்டது )
- யூத அரசு (c. 930 BC– 586 BC; பாபேல்இனால் வெற்றிகொள்ளப்பட்டது )
- ஏதென்ஸ் (c. 1000 BC - 683 BC)
- எசுபார்த்தா (c. 1300 BC - 192 BC)
- மக்கெடோனியா (பண்டைய இராச்சியம்) (808 BC - 148 BC)
- உரோமப் பேரரசு (753 BC - 509 BC)
- மகத நாடு (684 BC - 26 BC)
- பாரசீகப் பேரரசு (c. 648 BC - 334 BC; became subnational monarchy of Kingdom of Macedon)
- பாரசீகப் பேரரசு (323 BC - 1037 AD; became subnational monarchy of Sultinate of Seljuk)
- லைஜின் (Laigin), founded c. 300 BC - 1632.
- Greco-Bactrian Kingdom (250 BC - 125 BC; became குசான் பேரரசு)
- Empire of China (221 BC - 1912 AD; ended by revolution)
- Indo-Greek Kingdom (180 BC - 10 AD)
- மக்கபேயர் அரசுs (140 BC- 37 BC; succeeded by Herodian Dynasty)
- Herodian Dynasty (37 BC- 92 AD)
- Ulaid, c. 1st century BC - 1201
- குசான் பேரரசு (105 BC - 270 AD; became Kidarite Kingdom)
- Silla (57 BC - 935 AD)
- Goguryeo (37 BC – 668 AD)
- உரோமைப் பேரரசு (31 BC - 476 AD)
- Baekje (c. 18 BC - 660 AD)
- Funan (c. 1st century AD - c. 7th century; absorbed into Khmer Empire)
- Gangga Negara (c. 1st century - 1026)
- Indo-Parthian Kingdom (c. 1st century - c. 106)
- Västergötland (c. 1st century - c. 6th to 12th century; absorbed by சுவீடன்)
- Aidhne (pre-1st century - 1543)
- Sri Ksetra (c. 1st century - 656)
- Cóiced Ol nEchmacht - pre 2nd century AD to c. 600.
- Chera Kingdom (c. 3rd century BC - 1102 AD; became Kingdom of வேணாடு)
- Chola Kingdom (c. 3rd century BC - 1279 AD; absorbed into பாண்டியர்)
- சிறீவிஜயம் (c. 3rd century AD - c. 1400; became மலாக்கா சுல்தானகம்)
- Sassanid Empire (226 - 651; a period of Persian Empire)
- குப்தப் பேரரசு (240 - 550)
- Kingdom of Osraige, c.4th century - c. 1556.
- Kingdom of Uí Failghe, at least 4th century - 16th century.
- Shogun (c. 12th century - 19th century)
- Unification of Japan (c. 16th century)
- Kedah Kingdom (630 - 1136; became Kedah Sultanate )
- Kidarite Kingdom (c. 4th century - c. 5th century)
- Kingdom of Powys (c. 4th century - 1284; absorbed into England)
- பைசாந்தியப் பேரரசு (324 - 1453; absorbed into உதுமானியப் பேரரசு)
- Uí Maine, Ireland, c.357-c.1611.
- Munster (c.300-12th century)
- Kingdom of Gwynedd (c. 5th century - 1209; absorbed into Wales)
- Connacht (4th/5th century - 1478)
- Máenmaige (pre 581-8th/9th century)
- Suebi (410 - 584)
- Tethbae (pre 5th - 11th century)
- Merovingians (410 - 751)
- Ailech (5th-century - 1185)
- Visigothic Kingdom (475 - 718)
- Ostrogothic Kingdom (489 - 553; absorbed into Byzantine Empire)
- Kingdom of Terengganu (c. 6th century - c. 15th century; became subnational monarchy of மலாக்கா)
- Dál Riata (pre 6th century - 839)
- Pattani Kingdom (c. 500 - c. 11th century; became subnational monarchy of சிறீவிஜயம்)
- Frankish Empire (509 - 843; became Holy Roman Empire)
- Kingdom of Mide (c. 530's - 1173)
- Chenla (550 - c. 715)
- Mercia (585 - 918; absorbed into England)
- Ui Fiachrach Muaidhe (c. 600 - c.1603)
- Frisian kingdom (around 600 - 734; destroyed by the Franks.)
- Brega (pre 604 - 1171)
- Cnogba (Knowth) (pre 634-10th century)
- Conaille Muirtheimne (pre 668-after 1081)
- Kingdom of Breifne (6th century - 1605)
- Champa (c. 7th century - 1832)
- Sultanate of Brunei (c. 7th century - 1959; became absolute monarchy with a constitution)
- First Bulgarian Empire (681 - 1018; absorbed into Byzantine Empire)
- Airgíalla (pre 697 AD - 1590)
- Deis Mumhain (pre 697-c.1244)
- Balhae Empire (698 - 926)
Middle Ages and Renaissance
[தொகு]- Loch Gabhair (8th-11th century)
- Al-Andalus (711 - 1492; absorbed by Kingdom of Spain)
- Kingdom of Asturias (718 - 924; absorbed by Kingdom of León)
- Maigh Seóla (pre-752 AD. - 1051)
- Umaill (pre-773 AD - c. 1603)
- Sultanate of Morocco (780 - 1957; became constitutional monarchy)
- கெமர் பேரரசு (802 - 1431; became Khmer Kingdom)
- Kingdom of Axum (400 bc - 500;)
- High Kings of Ireland (c.800-1198)
- நவார் இராச்சியம் (824 - 1512; absorbed into Kingdom of Spain)
- Murcia (825 - 1243; became subnational monarchy of the Kingdom of Castile)
- புனித உரோமைப் பேரரசு (843 - 1806; dissolved after defeat by பிரான்சின் முதலாம் நெப்போலியன்)
- Kingdom of France (843 - 1791; became constitutional monarchy)
- Unification of Japan (16th century)
- Kingdom of Scotland (843 - 1707; united with இங்கிலாந்து இராச்சியம் to become பெரிய பிரித்தானிய இராச்சியம்)
- Pagan Kingdom (849 AD - 1364 AD)
- Kingdom of Dublin (853-1171)
- Kingdom of Norway (872 - 1814; became constitutional monarchy with the Swedish Sovereign as King)
- Kievan Rus' (882 - 1240; became Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia)
- Kingdom of León (913 - c. 13th century; absorbed into Crown of Castile)
- Goryeo Dynasty (918 - 1392; became Joseon Dynasty)
- Kingdom of Aragon (925 - 1162; became Crown of Aragon)
- Kingdom of Croatia (medieval) (925 - 1102)
- இங்கிலாந்து இராச்சியம் (927 - 1707; united with Kingdom of Scotland to become பெரிய பிரித்தானிய இராச்சியம்)
- Kingdom of Denmark (936 - 1848; became constitutional monarchy)
- Magh Luirg (c.956-c.1585)
- சுவீடன் (970 - 1866; became constitutional monarchy)
- Sultanate of Egypt (972 - 1517; became subnational monarchy of the உதுமானியப் பேரரசு)
- Kingdom of Castile (1037 - 1230; became Crown of Castile)
- Sultanate of Seljuk (A Dynasty established in Iran 1037–1307)
- Kingdom of Nri (1043—1911)
- Síol Anmchadha (pre 1066 - after 1567)
- Kingdom of வேணாடு (1102 - c. 1750)
- Thomond (1118-1543)
- Kingdom of Desmond (1118-1596)
- Kingdom of Portugal (1139–1910)
- Crown of Aragon (1162 - 1479; became Kingdom of Spain)
- Vladimir-Suzdal Grand Duchy (1168–1362; became Principality of Muscovy)
- Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396; absorbed into உதுமானியப் பேரரசு)
- Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia (1199–1349; absorbed into Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania)
- Despotate of Epirus (1204–1479; absorbed into உதுமானியப் பேரரசு)
- Empire of Nicaea (1204–1265; absorbed into பைசாந்தியப் பேரரசு)
- Empire of Trebizond (1204–1461)
- மங்கோலியப் பேரரசு (1206–1368)
- Principality of Wales (1208–1283; absorbed by England)
- Serb Kingdom (1217–1395; regal title not succeeded)
- Crown of Castile (1230 - 1479; became Kingdom of Spain)
- Aztec Empire (known to exist before 1233 Conquered by எசுப்பானியா 1521; Puppet monarchy through 1565)
- Sukhothai Kingdom (1238–1438; absorbed into Ayutthaya Kingdom)
- Lanna (1259 - 1939)
- Principality of Andorra (1278 - 1993; became constitutional monarchy)
- உதுமானியப் பேரரசு (1299 - 1923)
- Serbian Empire (1345–1371; dynasty extinct)
- Ayutthaya Kingdom (1350 - 1767; became Kingdom of Siam)
- Kingdom of Vidin (1356–1396; absorbed into the உதுமானியப் பேரரசு)
- Principality of Muscovy (1362–1576; became Tsardom of Russia)
- 1st Kingdom of Ava (1364–1527)
- Joseon Dynasty (1392-1897; became Korean Empire 1897-1910, then Japanese occupation)
- Ashanti (c. 1400 - 1900; became subnational monarchy of Gold Coast)
- மலாக்கா சுல்தானகம் (1400–1511; ended with Portuguese occupation)
- கிளாந்தான் (1411–1499; became subnational monarchy of மலாக்கா)
- சூலு சுல்தானகம் (1412 - 1898; occupied by the அமெரிக்க ஐக்கிய நாடு)
- Ryūkyū Kingdom (1429 - 1879; annexed to Japan)
- Khmer Kingdom (1431 - 1954; became Kingdom of Cambodia)
- Kingdom of Spain (1479 - 1812; became constitutional monarchy)
- ஈரான் (1500 - 1935; became Kingdom of ஈரான்)
- Sultanate of Maguindanao (1505 - 19th century; occupied by எசுப்பானியா)
- Bunyoro (c. 1520 - 1899; became subnational monarchy of the ஐக்கிய இராச்சியம்)
- Pegu Kingdom (1527–1531)
- ஜொகூர் சுல்தானகம் (1528 - 1946; became subnational monarchy of Malayan Union)
- Sultanate of Perak (1528 - 1874; became subnational monarchy of the ஐக்கிய இராச்சியம்)
- Maguindanao Sultanate (1205 - 19th century; annexed by எசுப்பானியா)
- சூலு சுல்தானகம் (1450 - 1936; incorporated into the Commonwealth of the Philippines)
- Taungoo Kingdom (1531 - c. 1610)
- Tsardom of Russia (1576–1721; became உருசியப் பேரரசு)
- 2nd Kingdom of Ava (1613–1752)
அரசாங்கம்
[தொகு]Systems of Governance
[தொகு]Presidential/Separated republics
[தொகு]These are systems in which a குடியரசுத் தலைவர் is the active head of the செயலாட்சியர் of government and is elected and remains in office independently of the சட்டவாக்க அவை. The following list includes democratic and non-democratic states:
Full presidential systems
[தொகு]In full presidential systems, the president is both head of state and head of government. There is generally no prime minister, although if one exists he or she serves purely at the pleasure of the president.
Presidential systems
[தொகு]- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
Presidential systems with a prime minister
[தொகு]- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag (Ivory Coast)
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag (Guinea-Conakry)
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag[1]
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
Semi-presidential systems
[தொகு]In semi-presidential systems, there is usually both a president and a prime minister. In such systems, the president has genuine executive authority, unlike in a parliamentary republic, but some of the role of a head of government is exercised by the பிரதமர். வார்ப்புரு:Colbegin
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag (சீனக் குடியரசு)
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
Parliamentary republics
[தொகு]A parliamentary republic is a system in which a பிரதமர் is the active head of the செயலாட்சியர் of government and also leader of the சட்டவாக்க அவை. The president's degree of executive power may range from being reasonably significant (e.g. Pakistan) to little (e.g. India) or none at all (e.g. Ireland). Where the president holds little executive power, his or her function is primarily that of a symbolic figurehead.
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag[2]
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag[3]
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag வார்ப்புரு:Small
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag வார்ப்புரு:Small
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag[4]
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
- வார்ப்புரு:Flag
செயற்படுத்தல்
[தொகு]- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.35 1.36 1.37 1.38 1.39 1.40 பிழை காட்டு: செல்லாத
<ref>குறிச்சொல்;type2என்னும் பெயரில் உள்ள ref குறிச்சொல்லுக்கு உரையேதும் வழங்கப்படவில்லை
- ↑ While the office of prime minister exists, the president is both the head of state and government.
- ↑ In Bangladesh, a caretaker government during parliamentary elections. The Caretaker government is headed by a Chief Adviser and a group of neutral, non-partisan advisers chosen from the civil society. During this time, the president has jurisdiction over the defence and foreign affairs ministries.
- ↑ Collective presidency consisting of three members; one for each major ethnic group.
- ↑ Formerly a semi-presidential republic, it's now a parliamentary republic according to David Arter, First Chair of Politics at Aberdeen University, who in his "Scandinavian Politics Today" (Manchester University Press, revised 2008), quotes Jaakko Nousiainen in "From semi-presidentialism to parliamentary government" in Scandinavian Political Studies 24 (2) p95-109 as follows: "There are hardly any grounds for the epithet 'semi-presidential'." Arter's own conclusions are only slightly more nuanced: "The adoption of a new constitution on 1 March 2000 meant that Finland was no longer a case of semi-presidential government other than in the minimalist sense of a situation where a popularly elected fixed-term president exists alongside a prime minister and cabinet who are responsible to parliament (Elgie 2004: 317)". According to the Finnish Constitution, the President has no possibility to rule the government without the ministerial approval, and substantially has not the power to disband the parliament under its own desire. Finland is actually represented by its Prime Minister, and not by its President, in the Council of the Heads of State and Government of the European Union.
